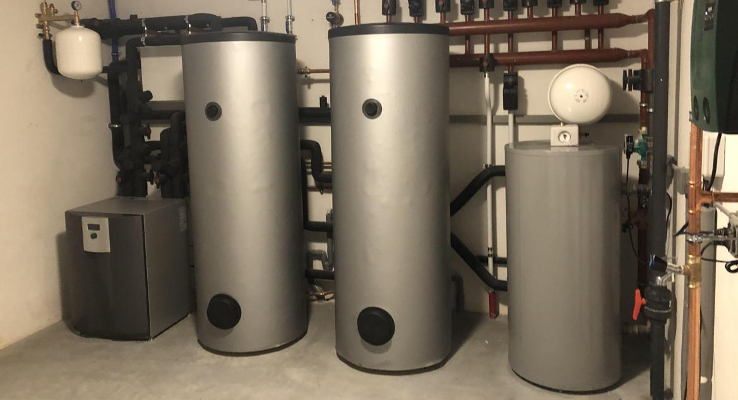
Both a buffer tank and a storage tank are meant for storage. But is there a crucial difference between the two, as different things are stored in them. This can result in annoying misunderstandings. Because maybe your customer thinks they know exactly what you are talking about, when in fact you are talking about two completely different applications! How do you prevent that?
The terms buffer tank and storage tank are regularly used interchangeably. Not convenient, because they are different devices, with different applications. Therefore, when contacting customers, as well as suppliers and peers, it is crucial to know that you are talking about exactly the same thing.
This is to avoid that you might later install a completely different device than the one the customer is waiting for. Check during each conversation whether you are really on the same page. If in doubt, keep asking until you know for sure what the expectations are and what is and is not intended.
Heat Storage
Essential to know and tell your customer is that a buffer tank is used in conjunction with something like a heat pump, solar collectors or PVT panels to store heat for later use. You can imagine that on warm, sunny days there is little need to turn on the heating. While the heat pump can run on free solar power just then.
A convenient solution is to temporarily store the generated heat in a buffer tank, allowing it to be used by the heating system at a later time. The heat pump then does not have to work, or at least less frequently and hard, once the sun is out of the picture again.
More efficient
The water in a buffer tank can easily stay warm for several days. So this is purely about heat storage intended for the central heating system. Regardless of whether it is something like radiators or underfloor heating. A buffer tank acts as a thermal mass and is also called a thermal battery. An additional advantage is that a buffer tank prevents what is known as commuting. This is the continuous switching on and off of the heat pump, which reduces the efficiency and life of a heat pump.
Domestic hot water
A storage tank, on the other hand, is designed to provide hot tap water, also called domestic water. Thus, this vessel contains water that is heated, then consumed somewhere in the home. Instead of the water just being a medium to transport heat (buffer tank). Other names regularly used for a storage tank are: boiler tank, domestic hot water heater, or hygiene buffer tank. Where the latter name could possibly add to the confusion again.
Together and yet alone
To further complicate matters, buffer tanks do exist that combine both functions. So heat storage for a heating system as well as supplying hot tap water. Quite convenient, because thanks to this integration, the customer can suffice with one extra large vessel, instead of having to install two different vessels in the often already limited space.
Depending on the type, in this case a heat exchanger is used to transfer the heat to the potable water, which in this way is thus passed through the buffer tank via a separate piping system. Another way is the so-called tank-in-tank solution. This time there is an additional tank in the buffer tank that is purely for domestic hot water. In all cases, the potable water remains strictly separated from the "heating water.